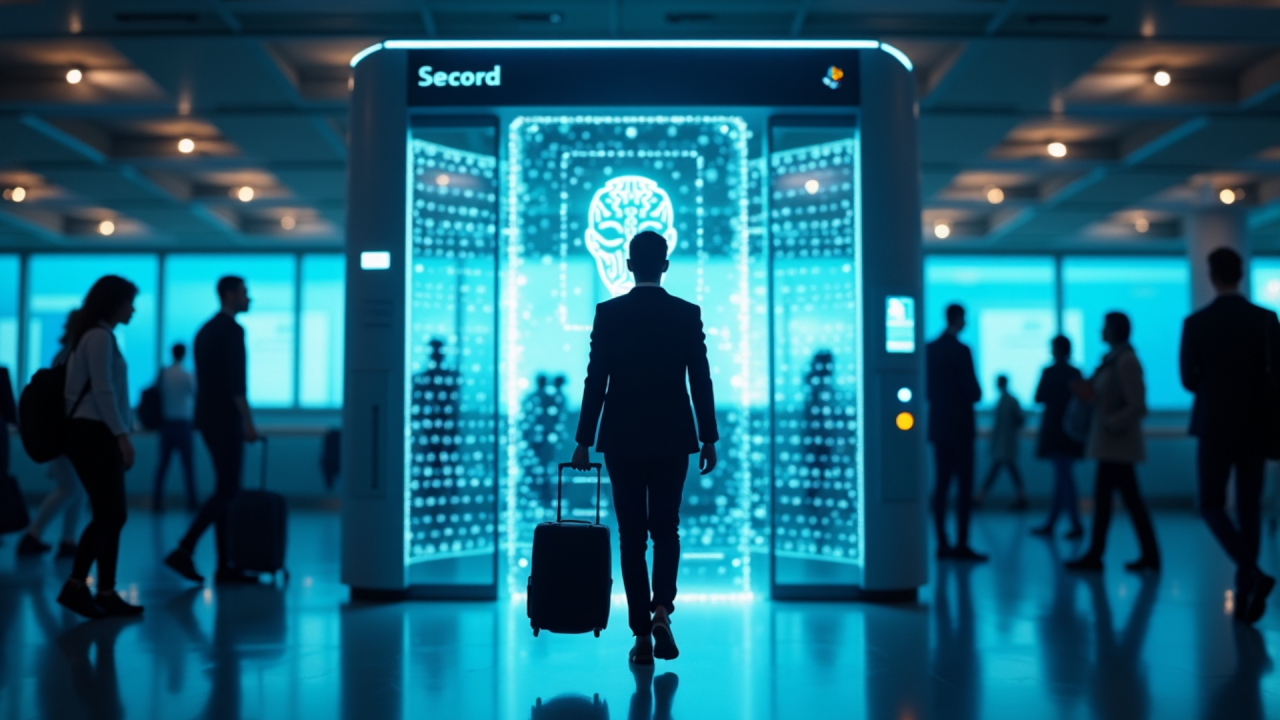
Biometric technology has become the cornerstone of border security in 2026, extending far beyond fingerprints and facial recognition. Today, immigration authorities are leveraging multi-modal biometrics, including iris scans, voice recognition, and behavioral pattern analysis. This multilayered approach ensures stronger identification of travelers and reduces the chances of identity fraud. Airports and border checkpoints are now equipped with seamless biometric corridors that allow passengers to move through immigration in minutes. This makes international travel more efficient, secure, and stress-free. For governments, the adoption of biometrics represents a leap forward in managing migration flows. These systems provide real-time monitoring of entries and exits, allowing countries to enforce overstays and visa violations more effectively. Authorities can also integrate biometric data with global security databases, ensuring individuals flagged for criminal or security concerns are detected instantly. This proactive approach strengthens national security while maintaining efficient processing for legitimate travelers.
Beyond security, biometric systems also improve user experience. Frequent travelers can enroll in trusted traveler programs, enabling near-instant clearance through automated checkpoints. For business travelers and tourists, this saves valuable time and improves the perception of a country’s immigration system. In addition, many governments are now rolling out mobile biometric enrollment, allowing applicants to submit biometric data through secure apps before traveling. This reduces congestion at border facilities and streamlines arrivals. Despite these advancements, concerns remain about privacy and data security. Biometric data is highly sensitive, and any breach could have long-term consequences for affected individuals. Governments are under pressure to invest in cybersecurity safeguards and maintain strict compliance with global privacy standards. The ethical debate surrounding biometric surveillance continues, as some fear it may lead to excessive tracking and loss of personal freedoms. The future of biometrics is expected to go even further, integrating artificial intelligence to analyze behavioral cues such as walking patterns, speech rhythms, and even emotional responses. While this promises even higher security, it raises important questions about civil liberties. The challenge for 2026 and beyond will be striking the right balance between national security, technological innovation, and the protection of individual rights.